This module is for Grades: 6-8 Welcome
The modern world has gone through periods of conflict, progress, war and peace. The more industrialized and stable countries are often referred to as developed countries because they have emerged with the most advanced economies and stable governments. Their “developed” status provides them with more wealth, rights and opportunities for their populations. Examples of developed countries include the United States, Japan and Great Britain.
The non-developed countries, or developing countries, have economies and governments that limit the standard of living for their populations. The term “developing” is used to classify countries in need of support to meet challenges and support their populations. There are many statistics used to identify which countries qualify as a “developing country.” Some of the factors include:
- A weak economy vulnerable to local or world events
- Less industrialization and technology compared to developed countries
- High unemployment rate of people who are able to work
- Low income and high poverty for the working class
- Poor medical care and social services
- A weak or corrupt government unable or unwilling to support a needy population
- Few democratic liberties or individual rights for citizens
These factors produce populations that have on average lower life expectancy, less education, and lower wealth when compared with developed countries.
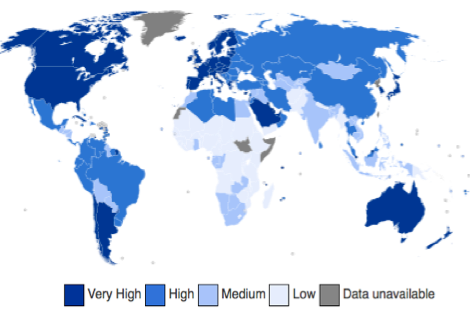
World map of human development.
Image Credit – Canuckguy et al. derivative work: Tomtom2732 via Wikimedia Commons Opens a new window
Focus Standard
WHST.6-8.2: Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/ experiments, or technical processes.
- Introduce a topic clearly, previewing what is to follow; organize ideas, concepts, and information into broader categories as appropriate to achieving purpose; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., charts, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension.
- Develop the topic with relevant, well-chosen facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples.
Skill
- Identify evidence from secondary sources that support a thesis statement.
Social studies students must be able to examine sources on modern issues such as developing countries, and respond to questions about issues using written essays. Social studies essays are written to prove an argument using evidence learned in the classroom and from sources such as textbooks and primary sources. An essay is often organized under a thesis statement, which categorizes evidence and introduces the rest of the essay. The activities in this module will use thesis statements to examine and organize evidence related to the challenges faced by developing countries.
Module Objective
By the end of this module, you will be able to:
- Identify economic, political and cultural issues facing developing countries in order to categorize evidence from secondary sources to support a thesis statement.